Wasps, Bees, and Hornets
Southern California is home to various stinging insects, each with unique characteristics and behaviors. Understanding the differences between wasps, bees, and hornets can help homeowners coexist with these insects. Many species of wasps including hornets are classified as ‘eusocial’ wasps. These insects work as a group to forage, construct nests, raise offspring, and protect the queen. The most commonly recognized nests are hanging paper nests, but some wasps like Yellowjackets make nests underground.
Learn How to Identify Stinging Insects
Stinging insects are more than just a nuisance; they play a crucial role in our ecosystem. Knowing the difference between them can help homeowners in the Western United States deal with them effectively.
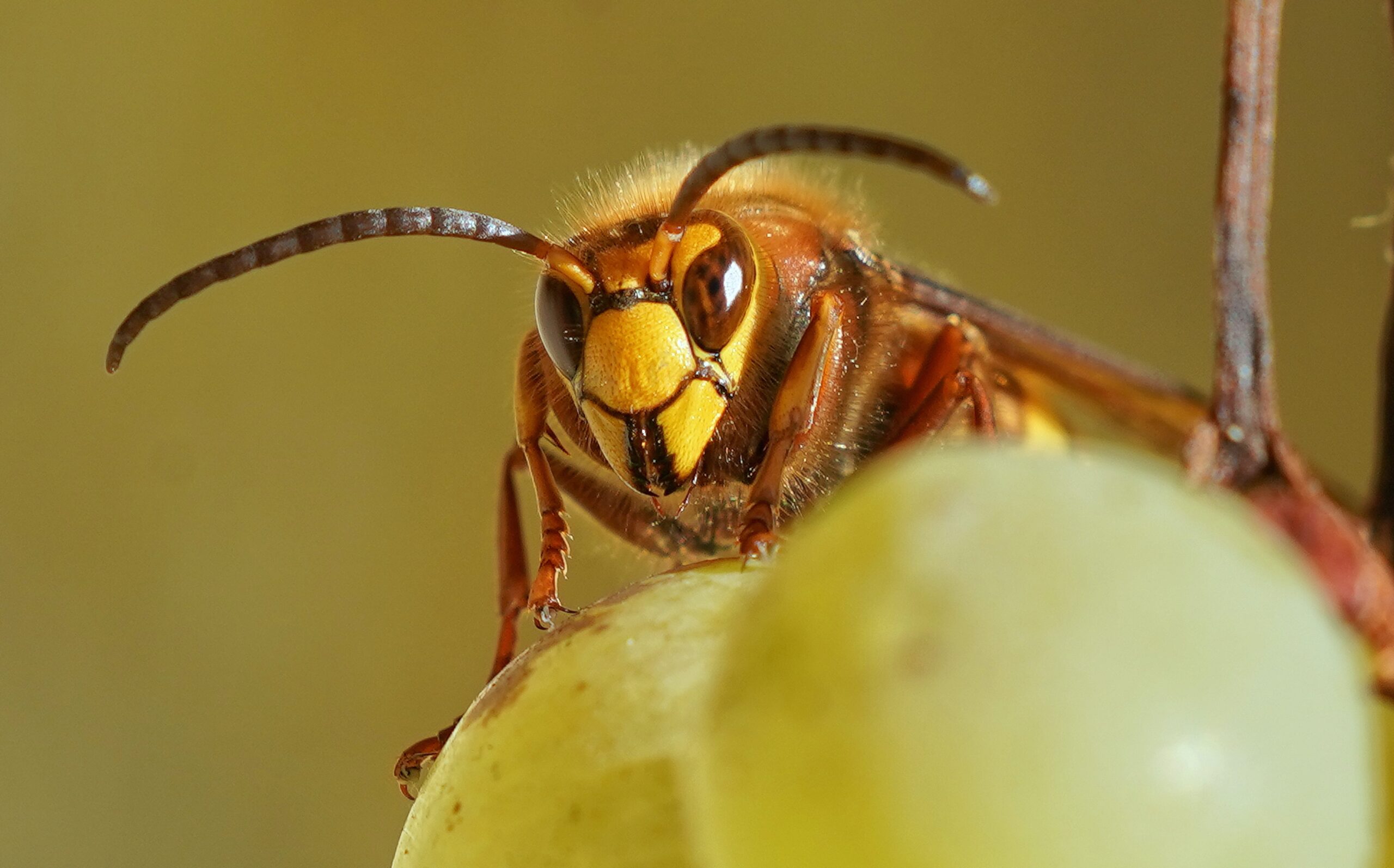
Hornets

Often confused with other stinging insects, hornets are a subset of wasps. They are larger, with robust, smooth bodies. Hornets are especially common in Southern California, with the Bald-faced Hornet being a notable species.
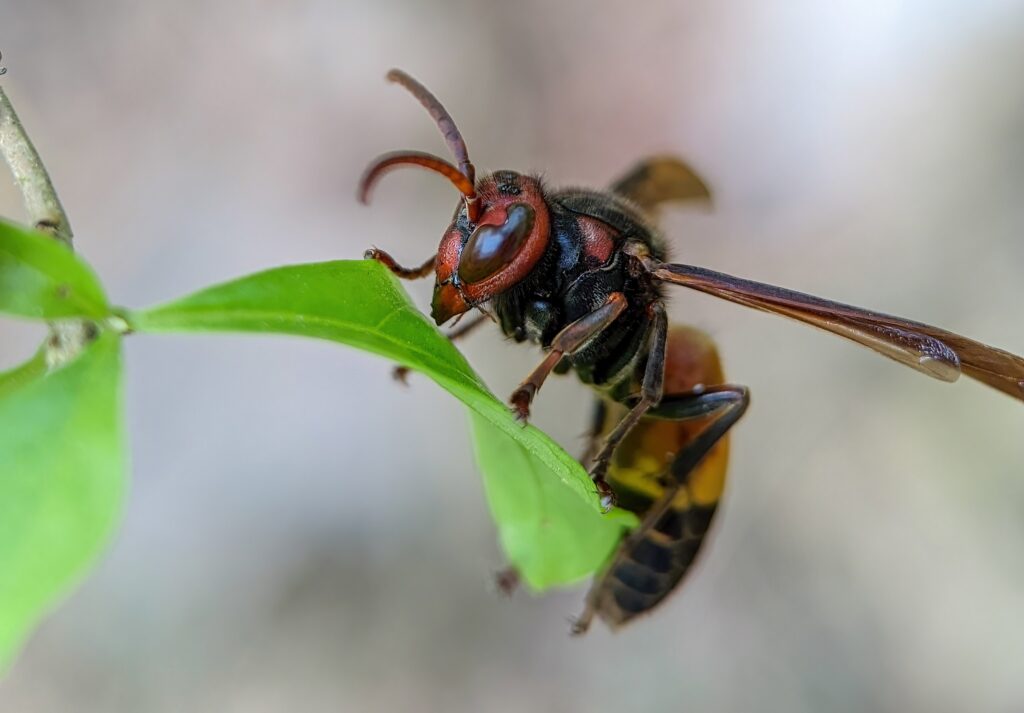
Wasps
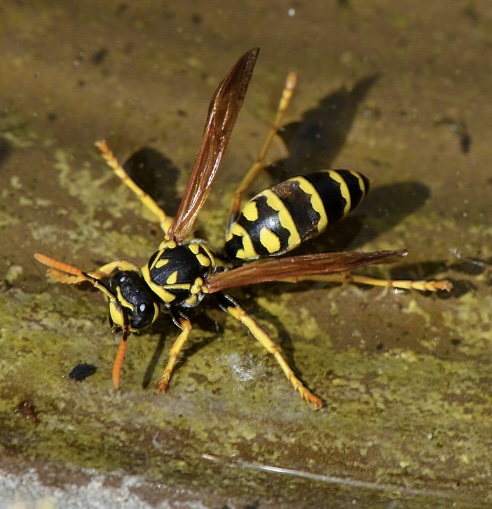

Wasps, a diverse group of insects, include Yellow Jackets and hornets. They vary in size, color, and behavior. Paper Wasps and Mud Daubers are common in Southern California and are known for their unique nests. They are smaller than hornets and are generally brighter in color.
Bees
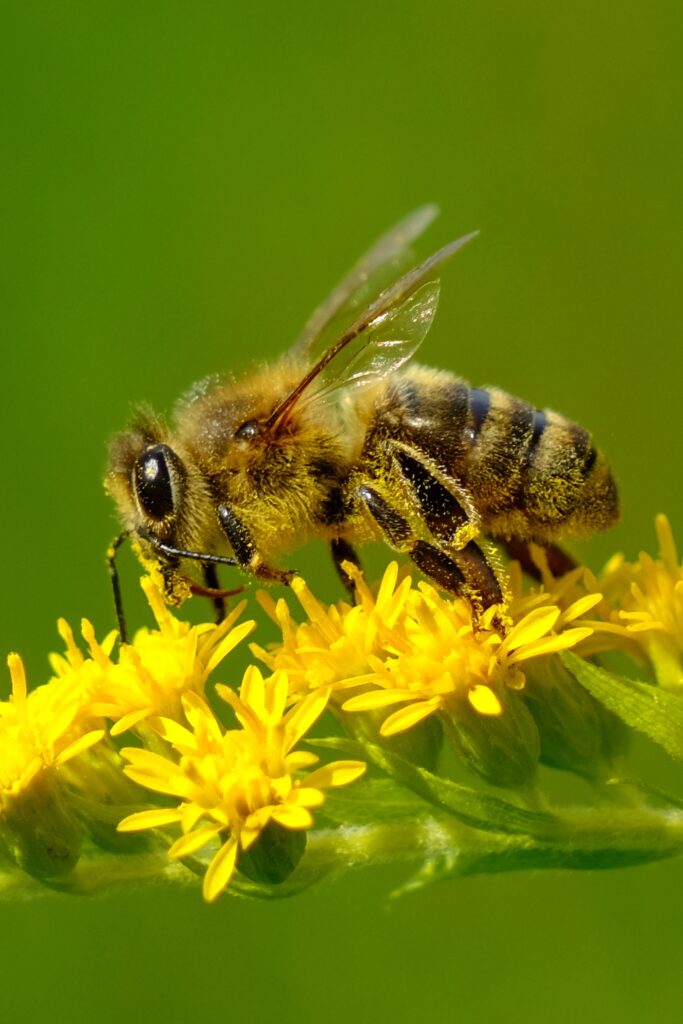

Unlike wasps and hornets, bees have hairy bodies and are usually more interested in pollinating plants than stinging. Common in the western United States are the Honey Bee and Bumblebee.
Identifying at a Glance
- Hornets: Large, robust, and often brownish in color.
- Wasps: Slender body with a noticeable “waist,” often yellow and black.
- Bees: Fuzzy, with a rounder body, mostly black and yellow.
Life Cycle
Wasps, bees, and hornets go through four main stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Their life cycles contribute to the local ecology by pollinating plants and controlling pest populations.
Wasps, Bees, and Hornets are Beneficial
These insects play vital roles in our environment. Bees are famous for pollination, while wasps and hornets help in pest control. For in-depth studies, check the University of California’s research on these insects.
Are Hornets and Wasps “Bad Bugs”?
While stings can be painful, hornets and wasps are not inherently “bad.” They contribute to controlling pests and maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Hornet, Wasp and Bee Stings
Hornets and wasps can sting repeatedly, unlike bees. Bees tend to sting for protection. Their stinger is barbed a can only be used once. Hornets and wasps have smooth stingers which they use for hunting. Because their stingers are not barbed, they are capable of stinging repeatedly, which can be dangerous for people with allergies. When their nest is threatened, they can sting repeatedly. They often attack in groups which makes them a formidable threat.
Yellow Jacket Alert: Taking the Sting Out of Fall

Understanding the difference between stings and bites is crucial. A sting injects venom, whereas a bite does not. Avoid wearing bright colors or floral patterns, and be mindful of food and drinks outdoors to avoid antagonizing these insects.
Beneficial Insects in the Garden
By understanding the role these insects play in our gardens, homeowners can learn to appreciate their presence rather than fear them.
More Like This
- Native Bees: The Best Pollinators for Your Garden
- Identifying Caterpillars in My Garden
- 9 Ways to Attract Bees, Butterflies, and Pollinators to the Garden